- Home
- Case Studies
- Container orchestration with Docker Swarm and Traefik
Container orchestration with Docker Swarm and Traefik
In the last few months, there were some rumors in regards to Docker Swarm and the future of that technology. However, based on the news published recently we can assume that Docker Swarm will be still supported. That's why I thought that it will be valuable for the community to present how you can use Docker Swarm to build a fully-fledged environment.
I don’t tell you that you have to use Docker Swarm. This is one of the options you choose among a few available orchestration tools. You can leverage Docker Swarm by installing Traefik that is an open-source router for microservice architectures and that article shows how to use those tools together.
What will you learn reading that article:
- how to install and configure Traefik 2 that is absolutely different compared to version 1
- how to deploy multi-tier application stack that includes Traefik that expose services to the internet, web server e.g. Nginx and backend we will go through canary deployments using a built-in feature in Traefik.
Prerequisites:
- up and running Docker Swarm cluster that has a public IP address. I recommend building your lab using infrastructure that is reachable via public IP addresses. It is even in accordance with 12 factor app manifest that all environments should be as similar as is possible.
- a possibility to create DNS entries for any domain; we will use entries, technically speaking URLS to access our Lab environment
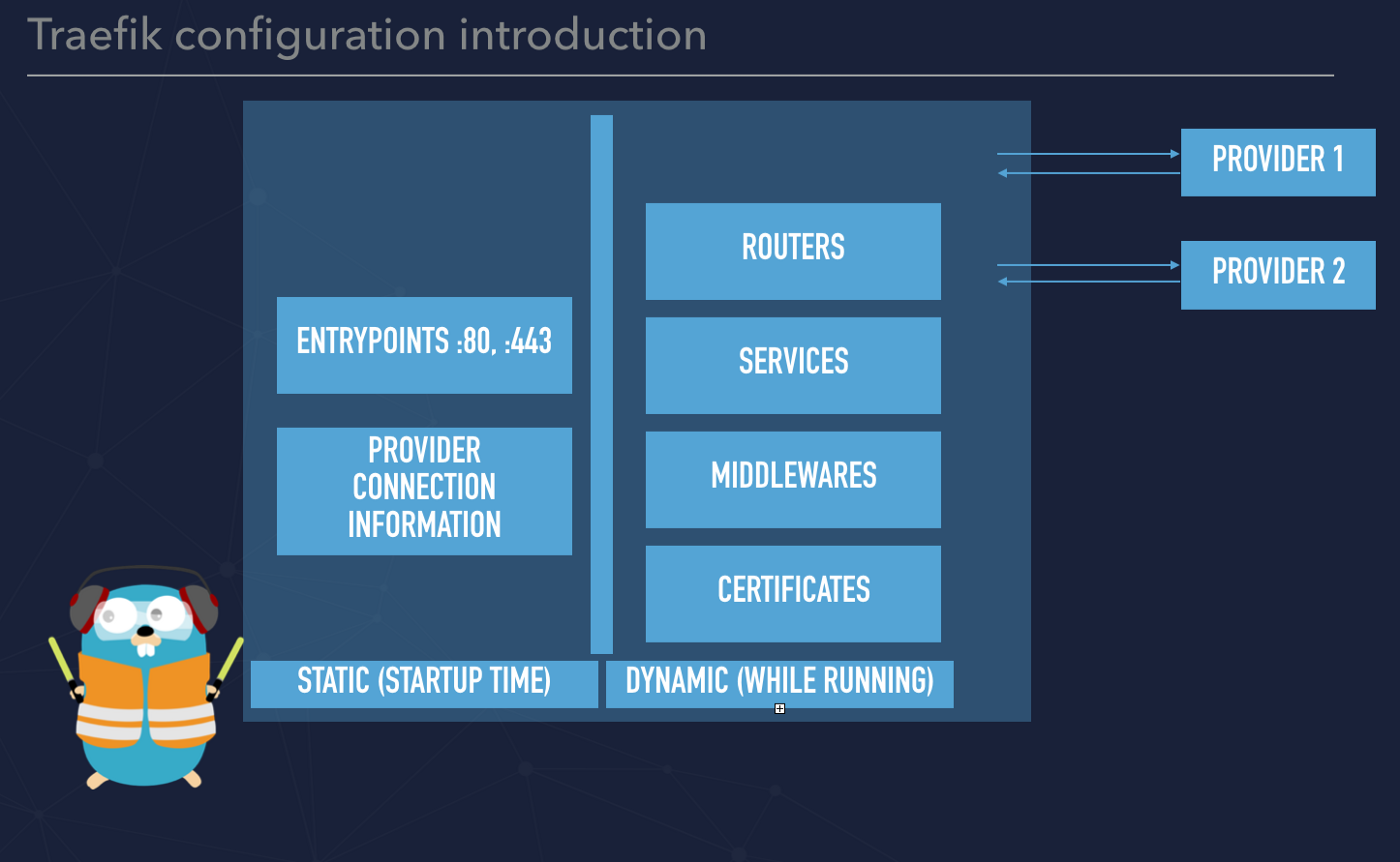
Traefik 2.x key features
Before moving forward, a few words what is it Traefik? This is a router that can be installed on the top of your infrastructure and expose services to your users. Each incoming request that is being sent to your infrastructure can be caught by Traefik and routed accordingly to the specific service. Typically, service is represented by a few instances of running containers. Despite the fact that Traefik can listen on port 80 and 443 (or even more ports) that are used for HTTP and HTTPS it is not web server as it is Nginx or Apache. Basically speaking Traefik catches a request, processes the request and route the request deeper to your infrastructure. By the end of 2019, there was a release of Traefik 2 that introduces a few crucial changes. The most important is to change the naming of key features of the system. If you are familiar with Traefik v.1 you probably know to name such as fronted, backend and rules.
In V 2 we have:
- router that replaced fronted
- service that replaced backend
- middleware that replaced rules
One of the features that have been added in the version is canary deployment. That is, in fact, routing incoming traffic between services based on the specified weights in a config file.
One of the common options is using CLI and pass the configuration through arguments.
Please also note that configuration can be split into two different things:
- fully dynamic routing configuration
- and static configuration that can be referred to as static
In order to simplify that you can think about the static configuration that is not changed very often. Those are providers configuration (Docker, Kubernetes) and entrypoints. Those parameters are applied while Traefik is starting. Everything that relies on routing can be treated as dynamic and can be hot reloaded.
However, in my example configuration, I used dedicated configuration files to show a different approach. I also defined the directory with flag watch enabled. So each update to the files listed in this directory should automatically be reloaded without request interruption or connection loss.
See the definition of a docker stack file that runs Traefik.
1# docker stack deploy -c stack-tr-main.yml traefik --prune
2
3version: "3.7"
4services:
5 main:
6 image: traefik:v2.1.2
7 healthcheck:
8 test: wget --quiet --tries=1 --spider https://traefik.labs.cometari.eu/ping || exit 1
9 interval: 3s
10 timeout: 1s
11 retries: 3
12 start_period: 1s
13 ports:
14 - "80:80"
15 - "443:443"
16 configs:
17 # Dynamic config
18 - source: routers-config
19 target: /conf.d/routers.toml
20 - source: middlewares-config
21 target: /conf.d/middlewares.toml
22 - source: tls-config
23 target: /conf.d/tls.toml
24 - source: canary-config
25 target: /conf.d/canary.yml
26
27 # Static config
28 - source: traefik-config
29 target: /traefik.yml
30 networks:
31 - proxy-main
32 volumes:
33 - "traefik-certificates:/letsencrypt"
34 - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
35 deploy:
36 placement:
37 constraints:
38 - node.role == manager
39 - node.labels.traefik == true
40 update_config:
41 # https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/#update_config
42 order: start-first
43
44 labels:
45 - "traefik.enable=true" # Enable Traefik, because we disabled expose a service by default
46
47 - "traefik.http.routers.t.rule=Host(`traefik.labs.cometari.eu`)" # Tell Traefik to create routre 't' and catch all requests with given Host
48 - "traefik.http.routers.t.service=api@internal" # the router 't' will forward request to service api@internal
49
50 - "traefik.http.routers.t.tls.certresolver=le" # the router 't' will use TLS certresolver called LE
51 - "traefik.http.routers.t.entrypoints=websecure" # the router 't' should listen on both entrypoints
52
53 #- "traefik.http.services.t.loadbalancer.server.port=8080" # the router 't' will balance incoming requests between servers listens on port 8080
54 # - "traefik.http.services.t.loadbalancer.passhostheader=true"
55
56 - "traefik.http.routers.t.middlewares=authtraefik" # Tell Traefik, that for router 't' should use following middleware
57 - "traefik.http.middlewares.authtraefik.basicauth.users=admin:$$2y$$05$$1OX5jZ1Kpm/iVKE8tgUhu.STmPkgi0lLxVeP5yEcRioFdV4mcgdTu" # Tell Traefik to creat middleware for the give name with following credntails (bcrypt)
58
59 - "traefik.http.routers.http-catchall.rule=hostregexp(`{host:.+}`)" # global redirect to https
60 - "traefik.http.routers.http-catchall.entrypoints=web"
61 - "traefik.http.routers.http-catchall.middlewares=redirect-to-https"
62 - "traefik.http.middlewares.redirect-to-https.redirectscheme.scheme=https"
63
64 - "traefik.http.routers.ping.rule=Host(`traefik.labs.cometari.eu`) && Path(`/ping`)"
65 - "traefik.http.routers.ping.service=ping@internal"
66 - "traefik.http.routers.ping.tls.certresolver=le"
67 - "traefik.http.routers.ping.tls=true"
68
69 # Dummy service for Docker Swarm
70 - "traefik.http.services.dummy-service.loadbalancer.server.port=59999"
71
72networks:
73 proxy-main:
74 driver: overlay
75 attachable: true
76 name: proxy-main
77
78volumes:
79 traefik-certificates:
80
81configs:
82 routers-config:
83 name: routers-config-${CONFIG:-1}
84 file: ./conf.d/routers.toml
85 middlewares-config:
86 name: middlewares-config-${CONFIG:-1}
87 file: ./conf.d/middlewares.toml
88 tls-config:
89 name: tls-config-${CONFIG:-1}
90 file: ./conf.d/tls.toml
91 canary-config:
92 name: canary-config-${CONFIG:-1}
93 file: ./conf.d/canary.yml
94
95 traefik-config:
96 name: traefik-config-${CONFIG:-1}
97 file: ./traefik.yml
98
99
As you noticed I added a health check that is built-in feature into Traefik that is accessible via /ping endpoint. Swarm takes care of keeping Traefik in a healthy condition and in case of failing health check the process should be restarted.
Configuration of service through Labels
The simplicity of Traefik is the configuration and labels that I like the most. You can configure the behavior of Traefik adding specific labels on a container level and deploy the stack file.
Let’s go through the example configuration of Traefik (stack-tr-main.yml):
traefik.enable=true— we have to enable Traefik because in a static file we disabled to expose service automaticallytraefik.http.routers.t.rule=Host(traefik.labs.cometari.eu)— tell to Traefik to create router called ‘t’ catch all incoming requests specified in Host rules based on HTTP HOST header.traefik.http.routers.t.service=api@internal— the router‘t’should forward the request to service api@internal. This is a specific example because we are going to expose Traefik.traefik.http.routers.t.tls.certresolver=le— lets’ use CertResolver called LE that has been defined in a static file.traefik.http.routers.t.entrypoints=websecure— router‘t’should be available via websecure entrypointtraefik.http.routers.t.middlewares=authtraefik— lets assign middleware that is defined in a dynamic files. It just enabling basic auth for that servicetraefik.http.middlewares.authtraefik.basicauth.users=admin:<pass>— and here are credentials, remember to use bcrypt for generating passwordtraefik.http.routers.http-catchall.rule=hostregexp({host:.+})— lets’ catch-all requests and redirect them to HTTPS. Please note that we have just enabled a new router called http-catchall.traefik.http.routers.http-catchall.middlewares=redirect-to-https— we assigned the middleware called redirect-to-https for the newly created routertraefik.http.middlewares.redirect-to-https.redirectscheme.scheme=https— here is a redirection from HTTP to HTTPS.
Please refer to GIST — it should be more readable for you. I also added there a few comments.
There are many more configuration parameters that you can use and set in a label section, all of them are listed in Traefik’s documentation. However, you should know what are routers, services, and middleware and how easily you create them in a stack file.
Main configuration file with static settings
The main configuration file includes parameters that are set on startup. They can not be modified without restarting Traefik. I added more providers such as Swarm, File and Consul catalog. In your case, you can remove the consul catalog. As you can see I also defined directory /conf.d where I added additional files that can be dynamically updated without restarting Traefik.
Those files are stored in Docker Swarm Config and are versioned in stack files. Referring to Kubernetes you can use ConfigMaps to keep those files. You can see that in another article when I present how to work with Traefik and Kubernetes, literally speaking with K3S cluster.
I also created Entrypoints for HTTP, HTTPS, /ping and /metrics. There is also added LetsEncrypt configuration — you can consider using a staging environment for testing purposes.
1log:
2 level: info
3 format: json
4
5accessLog:
6 format: json
7 bufferingSize: 5
8
9providers:
10 docker:
11 watch: true
12 endpoint: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
13 exposedByDefault: false
14 swarmMode: true
15 network: proxy-main
16 swarmModeRefreshSeconds: 5
17
18 consulCatalog:
19 exposedByDefault: false
20 refreshInterval: 15
21 stale: true
22 cache: true
23 endpoint:
24 address: "http://consul-leader:8500"
25 scheme: foobar
26
27 file:
28 directory: /conf.d
29 watch: true
30
31entryPoints:
32 web:
33 address: ":80"
34 forwardedHeaders:
35 insecure: true
36
37 websecure:
38 address: ":443"
39 forwardedHeaders:
40 insecure: true
41
42 ping:
43 address: ":8082"
44 metrics:
45 address: ":8083"
46
47ping:
48 entryPoint: ping
49
50metrics:
51 prometheus:
52 entryPoint: metrics
53
54certificatesResolvers:
55 le:
56 acme:
57 email: kuba@cometari.com
58 storage: /letsencrypt/acme.json
59 tlsChallenge: true
60
61api:
62 dashboard: true
63
See the GIST with that configuration file.
Additional configuration files that are dynamic
- tls.toml — additional configuration in order to have better marks for SSL certificates.
- routers.toml — you can also use Traefik to route traffic for VM’s running in an old way, I mean not in a container. Here you can find an example of how to manage that. It can be useful if you are in the process of migrating from the infrastructure managed in the traditional way to container.
- middlewares.toml — here are middleware defined that can be attached in sections where you define routers
SSL Certificates and high availability
Due to the fact, we are in a containers world and each container should be immutable we should not have any persistence storage in our stack. However, in order to take advantage of Let’s Encrypt that is built-in into Traefik we need to store in a file our certificates. That’s why in an example configuration we defined volumes where a file with certificates will be stored. In that case, it is difficult to scale up horizontally Traefik to provide high availability because another instance of Traefik needs to have access to the file stored on a local volume.
If you need HA you can consider Traefik EE that has already built-in that feature or you can try to configure Cert Manager and provide HA based on that.
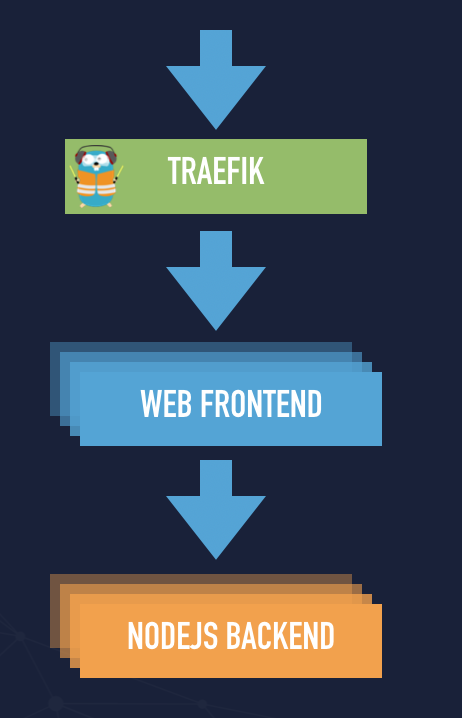
An example application stack
It is a simple application stack that consists of Nginx and a simple NodeJs backend. It is nothing sophisticated but gives you an overview that you can build a simple application even on Docker Swarm and Traefik can empower your application stack.
Here is the stack file:
1#docker stack deploy -c stack-app.yml app --with-registry-auth --prune 2version: "3.7" 3 4services: 5 backend: 6 image: jakubhajek/nodejs-backend:latest 7 healthcheck: 8 test: wget --quiet --tries=1 --spider http://localhost:3000/ || exit 1 9 interval: 3s 10 timeout: 1s 11 retries: 1 12 start_period: 5s 13 networks: 14 - app 15 deploy: 16 mode: replicated 17 replicas: 2 18 update_config: 19 failure_action: rollback 20 parallelism: 1 21 delay: 5s 22 restart_policy: 23 condition: on-failure 24 delay: 5s 25 max_attempts: 3 26 resources: 27 limits: 28 memory: 128M 29 30 frontend: 31 image: nginx:1.17-alpine 32 healthcheck: 33 test: wget --quiet --tries=1 --spider http://localhost:80/ || exit 1 34 interval: 3s 35 timeout: 1s 36 retries: 3 37 start_period: 5s 38 networks: 39 - app 40 - proxy-main 41 configs: 42 - source: nginx_config 43 target: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 44 deploy: 45 mode: replicated 46 replicas: 2 47 update_config: 48 failure_action: rollback 49 parallelism: 1 50 delay: 10s 51 restart_policy: 52 condition: on-failure 53 delay: 10s 54 max_attempts: 3 55 labels: 56 - "traefik.enable=true" 57 - "traefik.http.routers.myapp.rule=Host(`node-app.labs.cometari.eu`)" 58 - "traefik.http.routers.myapp.tls.certresolver=le" 59 - "traefik.http.routers.myapp.entrypoints=websecure" 60 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.server.port=80" 61 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.passhostheader=true" 62 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.healthcheck.path=/healthcheck" 63 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.healthcheck.interval=100ms" 64 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.healthcheck.timeout=75ms" 65 - "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.healthcheck.scheme=http" 66 resources: 67 limits: 68 memory: 128MB 69 70configs: 71 nginx_config: 72 name: nginx-config-${NGINX_CONFIG:-1} 73 file: ./nginx.conf 74 75networks: 76 app: 77 driver: overlay 78 name: app 79 attachable: true 80 driver_opts: 81 encrypted: "true" 82 proxy-main: 83 external: true 84
See the original Gist
Again, referring to the section label in service called fronted we can say that Traefik is going to do the following
- enable exposing that service
- create a router called myapp
- catch all request based on the given host
- enable both entrypoints web and websecure Works like a charm and seems that it is pretty straightforward :)
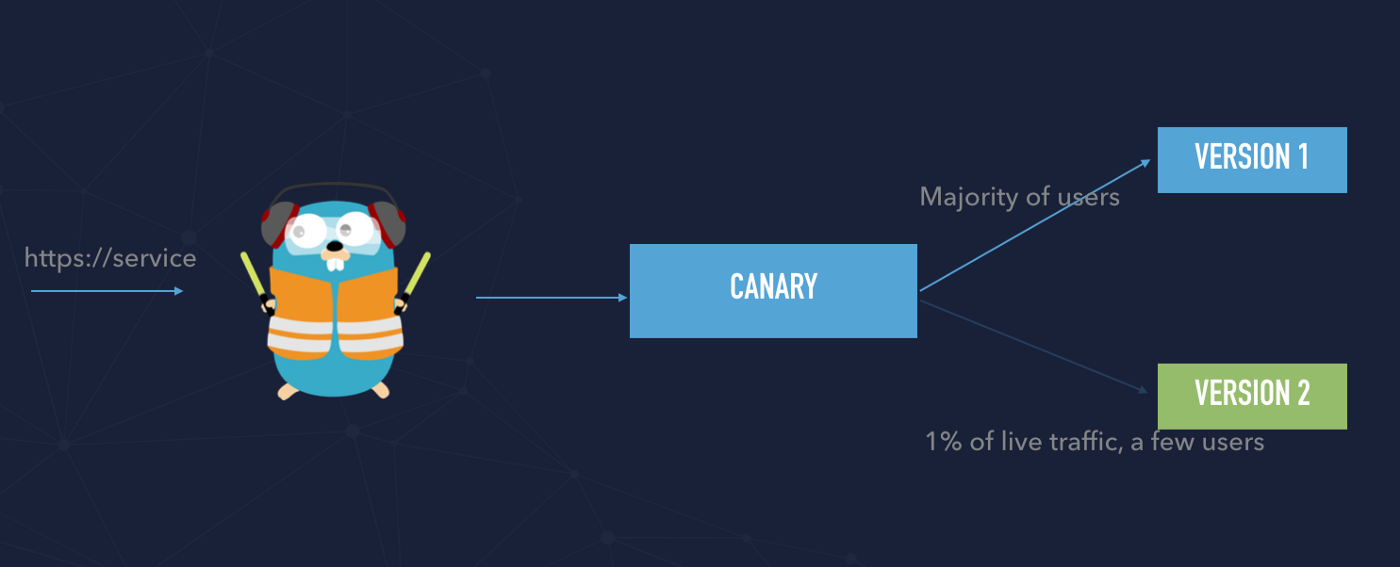
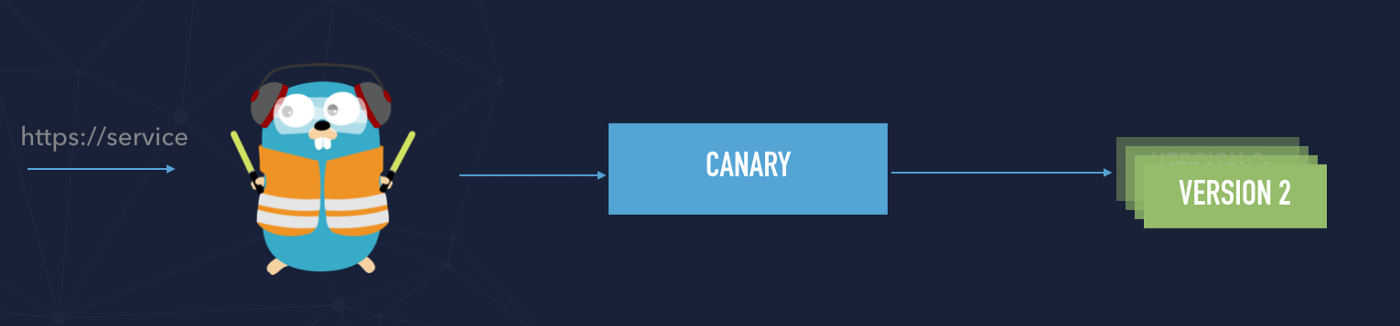
Canary deployments
In order to understand canary deployment, we have to understand the difference between release and deployments. See the diagram below. Technically speaking we can a few versions of our service deployed to our infrastructure. That means that deployment brings new code to the production environment but there is no production traffic yet.
Once the new deployment has been successfully tested and we ensured that a new version has no impact on our users we can decide to release the new version. It means that release brings live traffic to deployment — to the newest version of the application.
Canary deployments need some time to fully release and switch to the newest version of the entire traffic and definitely should be automated.
The service definition for canary deployment
In order to proceed with that approach, we have to create a weighted service and balance incoming traffic between those two services.
See the example of that:
1# docker stack deploy -c stack-canary.yml canary --with-registry-auth --prune 2version: "3.7" 3 4services: 5 app1: 6 image: jakubhajek/app1-node:v1 7 healthcheck: 8 test: wget --quiet --tries=1 --spider http://localhost:3000/ || exit 1 9 interval: 3s 10 timeout: 1s 11 retries: 1 12 start_period: 5s 13 networks: 14 - proxy-main 15 deploy: 16 mode: replicated 17 replicas: 2 18 update_config: 19 failure_action: rollback 20 parallelism: 1 21 delay: 5s 22 restart_policy: 23 condition: on-failure 24 delay: 5s 25 max_attempts: 3 26 resources: 27 limits: 28 memory: 128M 29 labels: 30 - "traefik.enable=true" 31 - "traefik.http.routers.app1.rule=Host(`canary.labs.cometari.eu`)" 32 - "traefik.http.routers.app1.tls.certresolver=le" 33 - "traefik.http.routers.app1.entrypoints=websecure" 34 35 # Canary approach 36 - "traefik.http.routers.app1.service=canary@file" 37 38 - "traefik.http.services.app1_svc.loadbalancer.server.port=3000" 39 40 app2: 41 image: jakubhajek/app1-node:v2 42 healthcheck: 43 test: wget --quiet --tries=1 --spider http://localhost:3000/ || exit 1 44 interval: 3s 45 timeout: 1s 46 retries: 1 47 start_period: 5s 48 networks: 49 - proxy-main 50 deploy: 51 mode: replicated 52 replicas: 2 53 resources: 54 limits: 55 memory: 128M 56 labels: 57 - "traefik.enable=true" 58 - "traefik.http.services.app2_svc.loadbalancer.server.port=3000" 59 60networks: 61 proxy-main: 62 external: true 63
See the original GIST
We created two Swarm services:
- app1 — use docker image tagged as v1
- app2 — use docker image tagged as v2
The application is available through an example URL https://canary.labs.cometari.com We have defined that weights are defined in a separate configuration file, that line is responsible for that:
traefik.http.routers.app1.service=canary@file
Traefik will read the configuration from that file that is a part of dynamically updated. configuration:
1http: 2 services: 3 canary: 4 weighted: 5 services: 6 # Load balancing between Traefik services 7 - name: app1_svc@docker 8 weight: 1 9 - name: app2_svc@docker 10 weight: 5 11
Then in the service APP1, we have added following line:
traefik.http.services.app1_svc.loadbalancer.server.port=3000
Going forward in the service APP2, we had another line
traefik.http.services.app2_svc.loadbalancer.server.port=3000
That means that Traefik is going to balance incoming requests between those two services app1svc and app2svc. It will use weights defined in the file canary@file that is presented a few lines above. The entire source code of that is available on my Github repo:
https://github.com/jakubhajek/traefik-swarm-mastery
The entire workflow I presented during one of the Traefik online meetups, the link is below:
You don't’ have an influence on what applications (v1 or v2) your request is going to reach. However, if you would like to allow your testers to perform smoke tests on v2, you create middleware that adds a specific header, for example:
X-Canary-Header: “knock-knock”
then you have to assign that middleware to your new routing rule and use the following statement:
Host(`canary.labs.cometari.eu`) && HeadersRegexp(`X-Canary-Header`, `knock-knock`)
Make sure also that you assigned middleware that you have created.
That means that we are create routing rules using the HTTP HOST header and also HeadersRegexp. It works perfectly, just remember to add an HTTP header to your request that meets the criteria defined in the middleware.
I fully tested that approach with Traefik and its KubernetesCRD approach. It works like a charm!
Summary
Traefik is a great tool and connected with Docker Swarm can significantly empower your stack and the entire infrastructure. It provides a few important features:
- Auto-discovery can find and expose services to your users
- There are multiple ways to configure Traefik, there is no ready to use configuration, you can use file but also CLI arguments.
- Middlewares provides the possibility to customize your routes
- It integrates with every major cluster technology e.g. Swarm, Kubernetes
- Lets Encrypt is integrated so managing SSL certificates is easy. However, in the case of HA, you have to consider developing a solution using e.g. Cert Manager.
- Metrics are prepared in open metrics format so you can use Prometheus to create a dashboard
- Tracing is also available
- Rolling out releases thanks to the canary deployment
- Mirroring is also available so you can duplicate requests and route them to a different service.